The Medical Term That Means Inflammation Of A Vein Is
bustaman
Dec 03, 2025 · 16 min read
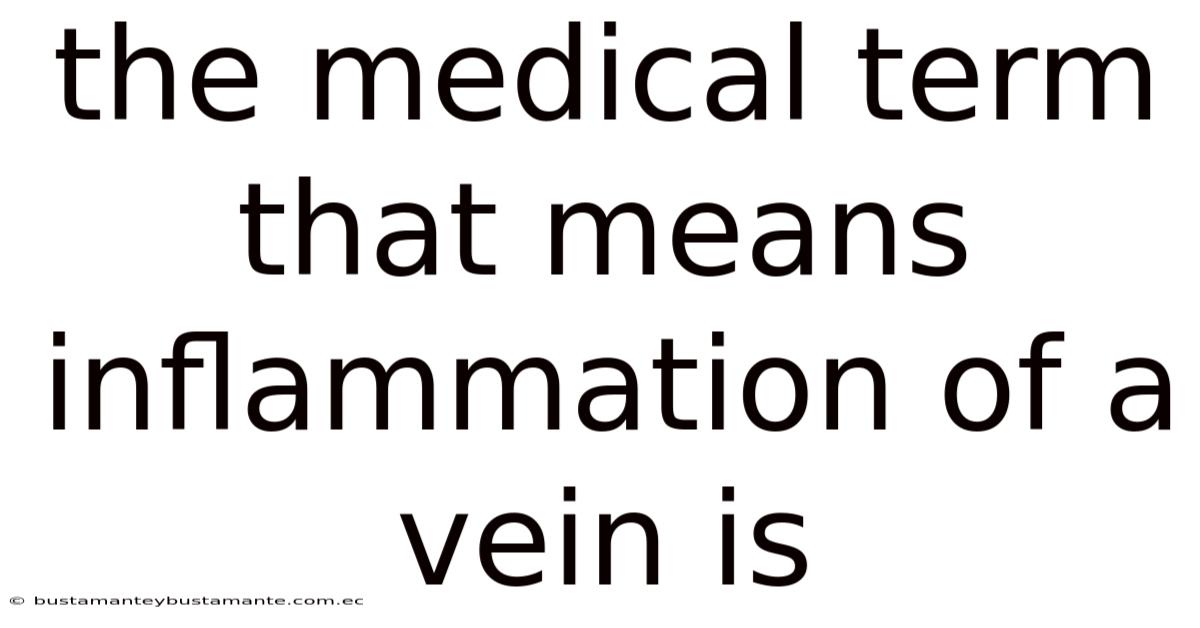
Table of Contents
Have you ever felt a throbbing pain or noticed a reddish streak along a vein? It might be more than just a minor discomfort. Vein inflammation can signal underlying issues needing attention. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes are the first steps toward managing your vascular health. This understanding empowers you to seek timely medical advice and explore effective treatments.
Imagine Sarah, a vibrant 45-year-old, who started experiencing discomfort in her lower leg. Initially, she dismissed it as muscle strain from her daily walks. However, the pain intensified, accompanied by redness and swelling along a prominent vein. Concerned, she consulted her doctor, who diagnosed her with phlebitis, the medical term for inflammation of a vein. Sarah’s story highlights the importance of early detection and proper medical intervention.
Main Subheading: Understanding Phlebitis
Phlebitis is the inflammation of a vein. The term comes from the Greek word phleps, meaning vein, and -itis, meaning inflammation. This condition can affect both superficial veins, which are close to the skin's surface, and deep veins, which are located deeper within the muscles. While superficial phlebitis is often less severe and more localized, deep vein phlebitis, known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), can lead to serious complications. Recognizing the differences and potential risks associated with each type is vital for effective management.
Phlebitis occurs when the lining of a vein becomes irritated and inflamed. This inflammation can result from various factors, including injury, infection, or prolonged inactivity. When the vein becomes inflamed, it can cause pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area. In some cases, a blood clot may form within the inflamed vein, leading to a condition called thrombophlebitis. Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors can help in preventing and managing this condition effectively. Proper diagnosis and timely treatment are crucial to alleviate symptoms and prevent potential complications.
Comprehensive Overview of Phlebitis
The term phlebitis refers to the inflammation of a vein, a condition that can range from mild discomfort to a more serious medical issue. To fully understand phlebitis, it is crucial to explore its definitions, scientific foundations, potential causes, and historical context. This comprehensive overview will provide a detailed perspective on this vascular condition.
Definitions and Types
Phlebitis is defined as the inflammation of a vein. It typically presents with symptoms such as pain, swelling, redness, and warmth along the affected vein. There are two primary types of phlebitis:
-
Superficial Phlebitis: This type affects veins located near the surface of the skin. It is often caused by local irritation, such as from an intravenous (IV) catheter. Symptoms are usually localized, and the condition is generally less severe.
-
Deep Vein Thrombophlebitis (DVT): This involves inflammation of veins located deep within the muscles. DVT is often associated with the formation of a blood clot (thrombus). It is a more serious condition because the clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism, which can be life-threatening.
Scientific Foundations
The scientific basis of phlebitis lies in the body's inflammatory response. When a vein is injured or irritated, the body initiates a cascade of biological processes to repair the damage. This process involves the release of inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines, which increase blood flow to the affected area. While this is a natural healing mechanism, excessive or prolonged inflammation can damage the vein and surrounding tissues.
In cases of thrombophlebitis, the inflammation is accompanied by the formation of a blood clot. This clot can further exacerbate the inflammation and impede blood flow. The coagulation cascade, a complex series of enzymatic reactions, leads to the formation of fibrin, the main protein component of a blood clot. Understanding these processes is essential for developing effective treatments that target both inflammation and clot formation.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing phlebitis:
- IV Catheters: Prolonged use of IV catheters can irritate the vein lining, leading to inflammation.
- Infections: Bacterial infections can directly inflame the vein.
- Injury: Trauma to a vein can cause inflammation and potentially lead to clot formation.
- Prolonged Inactivity: Sitting or lying down for extended periods can slow blood flow, increasing the risk of clot formation. This is particularly relevant for long flights or bedridden patients.
- Surgery: Post-operative patients are at a higher risk due to reduced mobility and increased clotting factors.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions such as varicose veins, cancer, and autoimmune diseases can increase the risk.
- Medications: Some medications, like birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy, can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of clot formation.
Historical Context
Phlebitis has been recognized as a medical condition for centuries, although the understanding of its causes and treatments has evolved significantly over time. In the past, phlebitis was often attributed to imbalances in the body's humors, a common belief in ancient medicine. As medical science advanced, researchers began to identify the role of inflammation and blood clots in the development of phlebitis.
The discovery of anticoagulants, such as heparin and warfarin, in the 20th century revolutionized the treatment of thrombophlebitis. These medications help prevent the formation and growth of blood clots, significantly reducing the risk of serious complications like pulmonary embolism. Modern imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and MRI, have also improved the diagnosis and management of phlebitis.
Essential Concepts
Several essential concepts are crucial for understanding phlebitis:
- Inflammation: The body's response to injury or infection, characterized by redness, swelling, pain, and warmth.
- Thrombosis: The formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system.
- Embolism: The blockage of an artery by a dislodged blood clot, air bubble, or other obstruction.
- Anticoagulation: The process of preventing blood clot formation, often achieved through medications.
- Venous Insufficiency: A condition in which the veins have difficulty sending blood from the limbs back to the heart, leading to blood pooling and potential complications.
By grasping these definitions, causes, and historical developments, individuals can better understand phlebitis and its implications for vascular health. Early detection and appropriate management are key to preventing complications and maintaining a good quality of life.
Trends and Latest Developments in Phlebitis Treatment
In recent years, there have been several notable trends and advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of phlebitis. These developments aim to improve patient outcomes, reduce complications, and enhance the overall management of this vascular condition. Staying informed about these trends is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals at risk of developing phlebitis.
One significant trend is the increasing use of minimally invasive procedures for treating both superficial and deep vein phlebitis. Traditional treatments often involved surgery, which can be invasive and require a lengthy recovery period. However, advances in medical technology have led to the development of less invasive options that offer comparable results with reduced risks and shorter recovery times.
Current Trends and Data
Recent data indicates a rise in the incidence of phlebitis, particularly among older adults and individuals with chronic medical conditions. This increase may be attributed to factors such as an aging population, higher rates of obesity, and increased use of central venous catheters for medical treatments. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has been linked to an elevated risk of thromboembolic events, including phlebitis, due to increased inflammation and coagulation abnormalities.
Studies have also shown that early diagnosis and intervention are critical for preventing complications associated with phlebitis. The use of advanced imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and CT venography, has improved the accuracy and speed of diagnosis, allowing for more timely treatment. Furthermore, the development of newer anticoagulant medications has expanded the treatment options available for managing thrombophlebitis.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures have become increasingly popular for treating phlebitis. These techniques involve using small incisions or catheters to access the affected vein and deliver targeted treatments. Some of the common minimally invasive procedures include:
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA): This procedure uses laser energy to heat and close off the affected vein. EVLA is typically used for treating superficial phlebitis caused by varicose veins.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Similar to EVLA, RFA uses radiofrequency energy to heat and seal the vein.
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: This involves using a catheter-based device to physically remove a blood clot from the vein. Mechanical thrombectomy is often used in cases of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) to quickly restore blood flow.
- Pharmacomechanical Thrombolysis: This combines mechanical thrombectomy with the local delivery of thrombolytic drugs to dissolve the clot.
Advancements in Anticoagulation
Anticoagulant medications play a crucial role in the treatment of thrombophlebitis by preventing the formation and growth of blood clots. Traditional anticoagulants, such as warfarin and heparin, have been used for decades, but they have certain limitations, including the need for frequent monitoring and dietary restrictions.
Newer anticoagulant medications, known as direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), offer several advantages over traditional anticoagulants. DOACs, such as rivaroxaban, apixaban, and dabigatran, are easier to administer, require less monitoring, and have fewer drug interactions. Studies have shown that DOACs are as effective as traditional anticoagulants for treating and preventing venous thromboembolism, including phlebitis, with a lower risk of bleeding complications.
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy remains a cornerstone of phlebitis management. Compression stockings help improve blood flow in the legs, reduce swelling, and prevent the recurrence of blood clots. Graduated compression stockings, which provide the greatest pressure at the ankle and gradually decrease pressure up the leg, are typically recommended.
Professional Insights
From a professional standpoint, the management of phlebitis requires a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach. Healthcare providers need to consider the patient's overall health, risk factors, and the severity of the condition when developing a treatment plan. Early diagnosis, appropriate anticoagulation, and lifestyle modifications are key to preventing complications and improving patient outcomes.
Additionally, patient education plays a vital role in the management of phlebitis. Patients should be educated about the signs and symptoms of phlebitis, the importance of adherence to treatment, and lifestyle measures to reduce the risk of recurrence. Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are also essential to ensure the effectiveness of treatment and detect any potential complications.
By staying abreast of the latest trends and developments in phlebitis treatment, healthcare professionals can provide the best possible care for their patients and improve their quality of life. The ongoing research and innovation in this field offer hope for even more effective and less invasive treatments in the future.
Tips and Expert Advice for Managing Phlebitis
Effectively managing phlebitis involves a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some practical tips and expert advice to help you manage the condition and prevent complications.
Seek Early Medical Attention
If you experience symptoms such as pain, swelling, redness, or warmth along a vein, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and reduce the risk of serious complications, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism. A healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
Delaying treatment can lead to more severe complications that may require more intensive interventions. Early intervention not only alleviates immediate discomfort but also safeguards your long-term vascular health.
Follow Your Treatment Plan
Adhering to your prescribed treatment plan is essential for managing phlebitis. This may include taking anticoagulant medications, wearing compression stockings, and following specific wound care instructions. Anticoagulants help prevent the formation and growth of blood clots, while compression stockings improve blood flow and reduce swelling. If you have any questions or concerns about your treatment plan, don't hesitate to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Consistency in following the treatment plan ensures that the medication works effectively and the healing process is optimized. Skipping doses or not wearing compression stockings as directed can undermine the treatment's effectiveness and prolong recovery.
Elevate Your Legs
Elevating your legs can help reduce swelling and discomfort associated with phlebitis. When sitting or lying down, elevate your legs above your heart level. This promotes blood flow back to the heart and reduces pressure in the veins of your legs. Use pillows or cushions to prop up your legs comfortably.
Elevation is a simple yet effective way to manage symptoms, especially after periods of prolonged standing or sitting. Making it a regular habit can significantly ease discomfort and aid in the healing process.
Stay Active
Regular physical activity is important for improving blood circulation and preventing blood clots. Engage in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling. Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing still. If you have to sit for extended periods, take frequent breaks to stretch your legs and walk around.
Physical activity helps maintain healthy blood flow and prevents stagnation, reducing the risk of clot formation. Even light exercises can make a significant difference in managing phlebitis symptoms.
Wear Compression Stockings
Compression stockings are a key component of phlebitis management. These stockings apply pressure to your legs, helping to improve blood flow and reduce swelling. Wear compression stockings as directed by your healthcare provider. They are most effective when worn throughout the day, especially during activities that involve prolonged sitting or standing.
Compression stockings come in different levels of compression; your healthcare provider will recommend the most suitable type for your condition. Consistent use of compression stockings can significantly alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing phlebitis. Excess weight puts additional pressure on your veins, making them more prone to inflammation and clot formation. Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Weight management not only reduces the risk of phlebitis but also improves overall cardiovascular health. Consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to develop a personalized weight management plan.
Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining healthy blood flow. Dehydration can thicken your blood, increasing the risk of clot formation. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Avoid sugary drinks and excessive caffeine, which can contribute to dehydration.
Hydration helps keep blood viscosity at an optimal level, facilitating smoother circulation and reducing the likelihood of clot formation. Make it a habit to drink water regularly, especially in warm weather or during physical activity.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots. If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your vascular health. Seek support from your healthcare provider or a smoking cessation program to help you quit.
Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of phlebitis and other cardiovascular diseases. The benefits of quitting smoking extend beyond vascular health, improving overall well-being and longevity.
Monitor Your Skin
Regularly inspect your skin for any signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or drainage. If you have a wound or ulcer, keep it clean and properly bandaged. Promptly treat any infections to prevent them from spreading to the veins.
Skin infections can exacerbate phlebitis and increase the risk of complications. Early detection and treatment of skin issues are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
By following these tips and expert advice, you can effectively manage phlebitis, reduce your risk of complications, and improve your overall vascular health. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and ongoing care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Phlebitis
Here are some common questions about phlebitis, along with concise and informative answers to help you better understand this condition.
Q: What is the main cause of phlebitis?
A: Phlebitis is primarily caused by inflammation of the vein, which can result from factors such as injury, infection, prolonged inactivity, or the presence of an IV catheter.
Q: How is phlebitis diagnosed?
A: Phlebitis is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, assessment of symptoms, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT venography to evaluate the affected vein.
Q: What are the common symptoms of phlebitis?
A: Common symptoms include pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and tenderness along the affected vein. In some cases, a palpable cord may be felt.
Q: Is phlebitis serious?
A: While superficial phlebitis is often less severe, deep vein thrombophlebitis (DVT) can be serious due to the risk of blood clots traveling to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
Q: What is the treatment for phlebitis?
A: Treatment options include pain relief with over-the-counter medications, compression therapy with stockings, elevation of the affected limb, anticoagulants to prevent blood clots, and, in some cases, minimally invasive procedures.
Q: Can phlebitis be prevented?
A: Yes, preventive measures include staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, wearing compression stockings, and staying hydrated.
Q: What are the risk factors for phlebitis?
A: Risk factors include prolonged inactivity, surgery, pregnancy, obesity, smoking, certain medical conditions (such as varicose veins and cancer), and the use of IV catheters or certain medications.
Q: How long does it take for phlebitis to heal?
A: The healing time varies depending on the severity and type of phlebitis. Superficial phlebitis may resolve within a few weeks, while DVT may require several months of treatment.
Q: When should I see a doctor for phlebitis?
A: You should see a doctor if you experience symptoms such as pain, swelling, redness, or warmth along a vein. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Q: Are there any home remedies for phlebitis?
A: While home remedies like elevation and warm compresses can provide relief, they should not replace medical treatment. Consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and management.
Conclusion
In summary, phlebitis, or the inflammation of a vein, is a condition that requires careful attention and management. Understanding the different types of phlebitis, its causes, and available treatments is essential for preventing complications and maintaining vascular health. Early diagnosis, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve outcomes. Remember, recognizing the symptoms early and seeking prompt medical advice are key to managing phlebitis effectively.
If you suspect you have phlebitis or have concerns about your vascular health, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Take proactive steps to manage your health, and don't hesitate to seek medical advice when needed. Your vascular health is an important part of your overall well-being.
Do you have any experiences or questions about phlebitis? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When Did The Twentieth Century Start
Dec 03, 2025
-
Benjamin Franklin And The Constitutional Convention
Dec 03, 2025
-
Maclaurin Series For Ln 1 X
Dec 03, 2025
-
How Do You Turn Fahrenheit Into Celsius
Dec 03, 2025
-
How To Find Point Of Inflection From First Derivative Graph
Dec 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Medical Term That Means Inflammation Of A Vein Is . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.