28 5 2 3 X 3
bustaman
Dec 06, 2025 · 10 min read
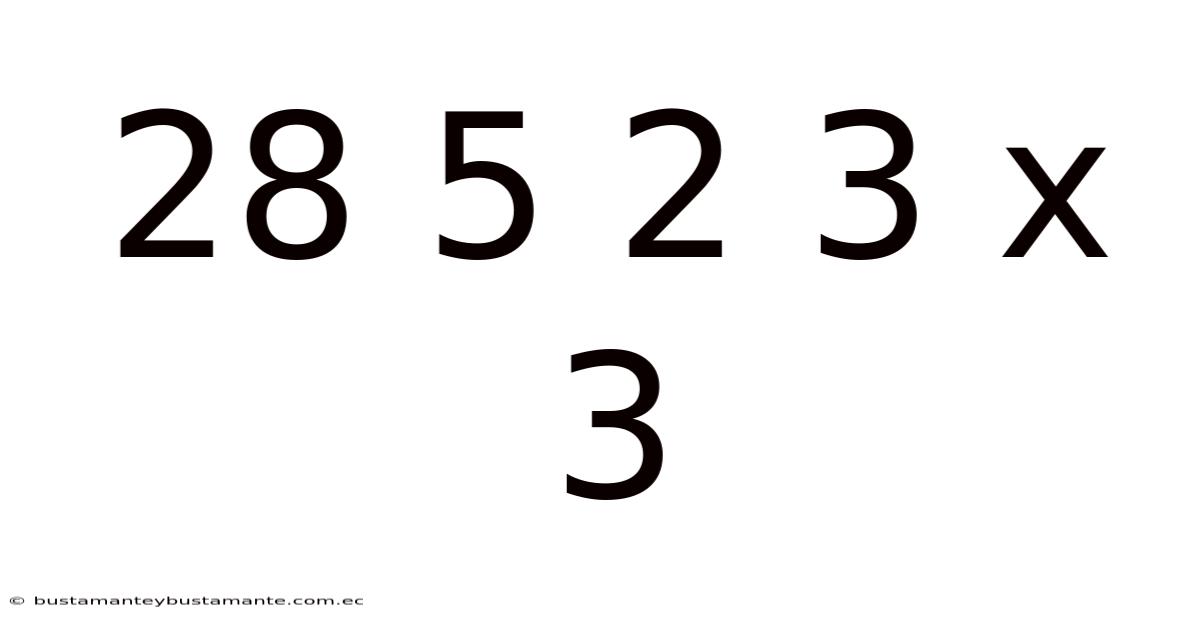
Table of Contents
The sequence 28 5 2 3 x 3 might appear like a random string of numbers and symbols at first glance. However, within this seemingly arbitrary combination lies the potential to unravel a fascinating puzzle. This article explores the various interpretations and possibilities associated with this sequence, ranging from its potential origins in mathematics and cryptography to its applications in other domains.
Main Subheading
At its core, the sequence 28 5 2 3 x 3 is a unique combination of numbers and an arithmetic operator. It could represent a simple mathematical expression, a segment of a larger dataset, a cipher awaiting decryption, or even a symbolic representation within a specific context. Understanding the possible meanings requires analyzing each component and exploring various interpretive frameworks. The 'x' could stand for multiplication, making it a direct calculation. However, without additional context, it is hard to determine its true meaning.
Comprehensive Overview
To fully understand the sequence 28 5 2 3 x 3, let's break down its components and examine different perspectives:
-
Numerical Components: The numbers 28, 5, 2, and 3 are integers with distinct properties. 28 is a composite number with several factors, including 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, and 28. The number 5 is a prime number, divisible only by 1 and itself. The number 2 is also a prime number and the only even prime number. Finally, the number 3 is also prime and has significance in numerous mathematical and cultural contexts.
-
Operator: The 'x' typically denotes multiplication in mathematics. However, depending on the context, it could also represent a variable, a cross-product in vector algebra, or even a placeholder for an unknown operation.
-
Mathematical Expression: If interpreted as a mathematical expression, 28 5 2 3 x 3 could be read in several ways, depending on the order of operations or intended groupings. Assuming the 'x' means multiplication, one primary interpretation could be:
- 28, 5, 2, 3, and 3 are individual elements, with 'x' indicating a multiplication operation between the last two numbers, 3 x 3. This interpretation suggests the sequence might be part of a larger calculation or dataset where the final step involves multiplying 3 by itself.
-
Cryptographic Significance: In cryptography, sequences of numbers are frequently used as part of encryption keys or ciphers. The sequence 28 5 2 3 x 3 might represent a segment of an encrypted message or a key used in an encryption algorithm. Without knowing the specific encryption method, it is difficult to decipher its meaning. It could be part of a substitution cipher, a transposition cipher, or a more complex algorithm involving mathematical operations.
-
Data Representation: In data analysis or computer science, number sequences are often used to represent specific information. The sequence 28 5 2 3 x 3 might be part of a data record, where each number represents a specific attribute or variable. For example:
- 28 could represent a date (e.g., the 28th day of a month).
- 5 could represent a quantity or a category.
- 2 and 3 could represent coordinates in a 2D space.
- The 'x 3' could indicate a scaling factor or a multiplier applied to some other data.
-
Symbolic Representation: Outside of technical contexts, the sequence 28 5 2 3 x 3 could have symbolic meaning, depending on cultural, artistic, or personal interpretations. Numbers often carry symbolic weight in various belief systems and artistic expressions. For instance:
- In numerology, each number is associated with specific attributes and energies.
- In art, numbers can be used to convey specific themes or messages.
- On a personal level, the numbers might represent significant dates, ages, or other personally relevant information.
-
Mathematical Interpretation: In pure mathematics, the sequence can be looked at in several ways:
- Discrete Mathematics: The sequence can be studied under discrete mathematics. Here, each number is treated as a separate entity. The multiplication operation can be seen as an operation between two elements of the sequence, altering or combining them.
- Number Theory: From a number theory perspective, properties of each number (prime, composite, even, odd) are critical. Exploring factors, divisibility, and modular arithmetic may lead to uncovering hidden relationships or patterns.
- Linear Algebra: If considered vectors or matrices, the sequence might represent components or transformations in a linear space. The 'x' could symbolize a matrix multiplication or a scalar multiplication.
-
Computational Context: Within computer science, the sequence can be used to define parameters or conditions within an algorithm.
- Programming: In code, 28 5 2 3 x 3 might be used to set loop conditions, array sizes, or to define conditional statements. The 'x' here would most likely be an operator.
- Data Structures: This sequence can represent the dimensions of a multi-dimensional array, parameters in a database query, or components of a complex data structure.
- Machine Learning: The sequence could be parameters for a machine learning model or part of a feature vector representing specific data points.
Trends and Latest Developments
While the specific sequence 28 5 2 3 x 3 may not appear directly in trending topics, its underlying principles are very relevant in numerous fields undergoing rapid development:
-
Cryptography and Data Security: The ongoing evolution of cryptographic techniques means number sequences remain fundamental in securing data. Quantum cryptography, blockchain technologies, and advanced encryption standards all rely on complex mathematical and computational processes using number sequences.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning heavily rely on numerical data and algorithms. Sequences of numbers are used for:
- Data Encoding: Transforming raw data into numerical representations that machine learning models can process.
- Model Parameters: Defining the structure and behavior of neural networks and other machine learning models.
- Optimization Algorithms: Updating model parameters to improve performance.
-
Big Data and Analytics: Big data involves analyzing large volumes of data to identify patterns, trends, and insights. Number sequences are often used to:
- Indexing and Sorting: Organizing and retrieving data efficiently.
- Time Series Analysis: Analyzing data points collected over time to predict future trends.
- Data Compression: Reducing the size of data for storage and transmission.
-
Financial Modeling: In finance, numerical sequences are critical for modeling market behavior, assessing risk, and making investment decisions. Algorithmic trading, quantitative analysis, and risk management all rely on sophisticated numerical techniques.
-
Quantum Computing: Quantum computing promises to revolutionize computation by leveraging quantum-mechanical phenomena. Number sequences play a key role in quantum algorithms, quantum error correction, and quantum cryptography.
Tips and Expert Advice
Working with number sequences like 28 5 2 3 x 3 requires a combination of analytical skills, domain knowledge, and practical tools. Here are some tips and expert advice:
-
Understand the Context: The most important step is to understand the context in which the sequence appears. Is it part of a mathematical problem, a cryptographic puzzle, a data record, or something else? Understanding the context will help you narrow down the possible interpretations and apply the appropriate tools and techniques.
-
Break It Down: Decompose the sequence into its individual components and analyze each one separately. Look for patterns, relationships, and properties that might provide clues to its meaning. Consider the mathematical properties of the numbers (prime, composite, even, odd), the possible meanings of the operators, and any other relevant information.
-
Consider Multiple Interpretations: Don't settle on the first interpretation that comes to mind. Explore multiple possibilities and evaluate each one based on the available evidence. Be open to unconventional or creative interpretations, especially if the sequence appears in a non-technical context.
-
Use Appropriate Tools: Depending on the context, use mathematical software, programming languages, or specialized tools for data analysis, cryptography, or other relevant domains. These tools can help you perform calculations, analyze patterns, and test different hypotheses.
-
Look for Patterns: Pattern recognition is essential when working with sequences. Use computational tools to look for patterns and anomalies in your data, which may point to an underlying structure or significance. Consider using statistical methods to identify recurring themes, cycles, or correlations.
-
Apply Critical Thinking: Evaluate each interpretation based on its plausibility, consistency, and explanatory power. Ask yourself whether the interpretation makes sense in the given context, whether it is consistent with other known information, and whether it provides a satisfactory explanation for the sequence.
-
Seek Expert Advice: If you're stuck, don't hesitate to seek advice from experts in relevant fields. Mathematicians, cryptographers, data scientists, and other specialists may be able to offer insights and guidance that you might not be able to obtain on your own.
-
Document Your Process: Keep a detailed record of your analysis, including the interpretations you considered, the tools you used, and the conclusions you reached. This will help you keep track of your progress, revisit your assumptions, and communicate your findings to others.
-
Learn the Fundamentals: Strengthen your foundational knowledge in mathematics, statistics, computer science, and other relevant fields. A solid understanding of these fundamentals will give you the tools and concepts you need to tackle complex problems involving number sequences.
-
Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest trends and developments in relevant fields. New techniques, tools, and discoveries are constantly emerging, and staying informed will help you stay ahead of the curve and tackle new challenges effectively.
FAQ
Q: What is the most common interpretation of a number sequence like 28 5 2 3 x 3?
A: The most common interpretation depends heavily on the context. It could be a mathematical expression, a piece of cryptographic data, or part of a larger dataset. Understanding the surrounding information is critical.
Q: How can I determine if a number sequence has cryptographic significance?
A: Look for randomness and complexity. Cryptographic sequences often appear random but are generated using specific algorithms. Analyzing the sequence for patterns and using cryptographic tools can help determine its significance.
Q: Is there a general method for deciphering number sequences?
A: No, there is no one-size-fits-all method. The approach depends on the context and potential interpretations. Start by breaking down the sequence, understanding the context, and considering multiple hypotheses.
Q: How do AI and machine learning use number sequences?
A: AI and machine learning use number sequences for data encoding, model parameters, and optimization algorithms. Sequences are used to represent data in a format that machine learning models can process.
Q: What tools are helpful for analyzing number sequences?
A: Tools include mathematical software (e.g., Mathematica, MATLAB), programming languages (e.g., Python, R), statistical software, and specialized tools for data analysis and cryptography.
Q: Where can I learn more about number sequences and their applications?
A: Universities, online courses, and professional training programs offer resources. Textbooks, research papers, and online communities in mathematics, computer science, and data science provide additional learning opportunities.
Q: What if the 'x' in the sequence does not represent multiplication?
A: The 'x' could be a placeholder, a variable, or represent a different operation depending on the context. Consider all possible meanings based on the surrounding information and potential applications.
Conclusion
The sequence 28 5 2 3 x 3, while appearing simple on the surface, embodies a wealth of potential interpretations and applications. From basic mathematical operations to complex cryptographic algorithms, understanding the context and applying appropriate analytical techniques is crucial. Whether used in data analysis, machine learning, or cryptography, number sequences are fundamental to modern technology and continue to play a vital role in solving complex problems.
To deepen your understanding, we encourage you to explore specific applications of number sequences in your field of interest. Try applying these concepts to real-world problems, and share your findings to enhance collective knowledge. What hidden insights can you uncover by analyzing the sequences around you?
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Plural Word For Deer
Dec 06, 2025
-
The Anatomy Of A Synapse Answer Key
Dec 06, 2025
-
Who Were The Big Four At The Paris Peace Conference
Dec 06, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In Water
Dec 06, 2025
-
Where Is The Division Symbol On Keyboard
Dec 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 28 5 2 3 X 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.